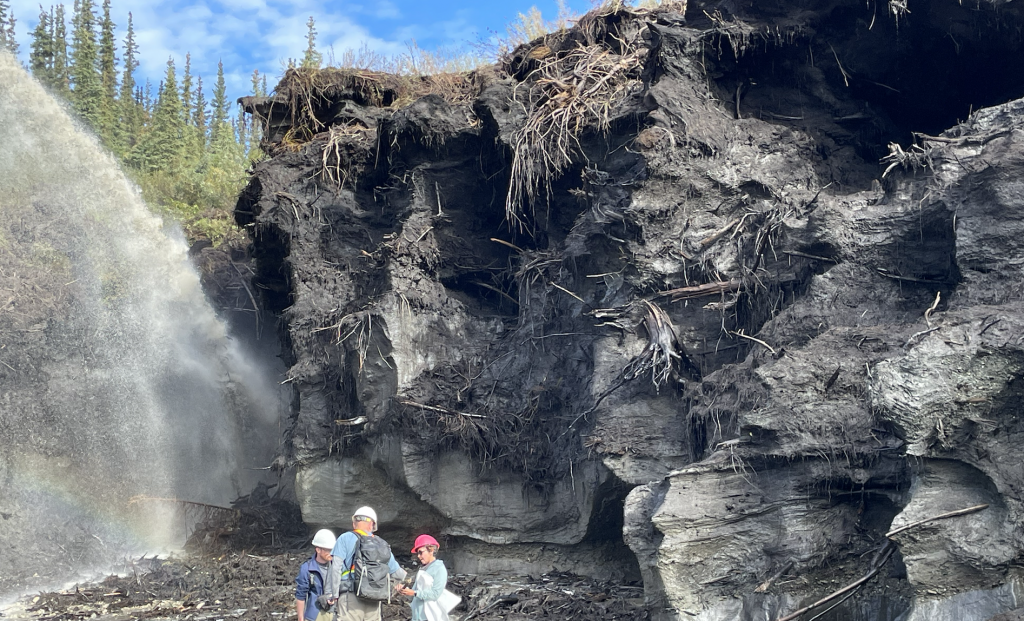
This past September we travelled to the Sahtu communities of Tulita and Deline to deliver workshops on climate change and permafrost for youth in the community with support from the Sahtu Secretariat and CIRNAC. We were also able to give community presentations on our work on permafrost in the area and hear alot about concerns and community observations. It was a productive and memorable trip
We had a busy but fulfilling day in Tulita working with ~20 youth in the classroom and outside, active layer probing and drilling cores with @OnTheLandry, @WedgeIceQc and Ashley Rudy of NTGS. Ending with a community dinner and talk on our work in the Sahtu, and community mapping. pic.twitter.com/ryu3O7O0nR
— duane froese (@tephrafan) September 28, 2022